Context
The Importance of Rainforests to our Survival
Rainforest Deforestation is the third largest emitter in the world
Source: World Resources Institute-By the Numbers: The Value of Tropical Forests in the Climate Change Equation by David Gibbs, Nancy Harris and Frances Seymour https://www.wri.org/insights/numbers-value-tropical-forests-climate-change-equation. Global Forest Watch https://www.globalforestwatch.org/map/
When you protect rainforests,
you also support global:
1. UN FAO – State of Forests 2020 – https://www.fao.org/state-of-forests/en/
2. Mo, L., Zohner, C.M., Reich, P.B. et al. Integrated global assessment of the natural forest carbon potential. Nature (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06723-z
3. Front. For. Glob. Change, 24 March 2022 Sec. Forest Disturbance Volume 5 – 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/ffgc.2022.756115
The Global Compliant Carbon Market
There are 3 different types of carbon markets: Regulated (ETS-Emissions Trading Schemes), Voluntary (VCM-Voluntary Carbon Market) and
the Paris Agreement Compliant Carbon Market (CCM).
The Three Types of Carbon Markets
Source: World Bank Carbon Pricing Dashboard https://carbonpricingdashboard.worldbank.org/ & Climate Focus Voluntary Carbon Market Dashboard https://climatefocus.com/initiatives/voluntary-carbon-market-dashboard/
Article 6 & ITMOs
The Compliatn Carbon Market (CCM) was established after
Article 6 of the Paris Agreement was signed by all 196 countries to establish a new carbon market mechanism. It allows governments to issue
Sovereign Internationally Transferable Mitigation Outcomes (ITMOs) and trade them bilaterally, or with the private sector.
The future carbon market opportunity and scalability is in this 73.8% global carbon emissions gap.
*INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION OF SECURITIES COMMISSIONS (IOSCO) defines the Paris Agreement Carbon Market as “…A compliance offset market. These are markets falling under Article 6.4 of the Paris Agreement; with the United Nations acting as the Supervisory Authority.”
What are Compliant Carbon Credit ITMOs?
Compliant Carbon Credit ITMOs are a carbon reduction/removal unit created under the UNFCCC Paris Agreement.
These have unique attributes compared to other carbon credits.
The Carbon Credit Matrix
Unlike other Carbon Credits, Compliant Carbon Credit ITMOs are in the Top-Right corner of the Carbon Credit Matrix: (x-axis Carbon Impact & y-axis Carbon Scalability). ITMOs can only be National at scale, and a Reduction and/or Removal carbon unit.
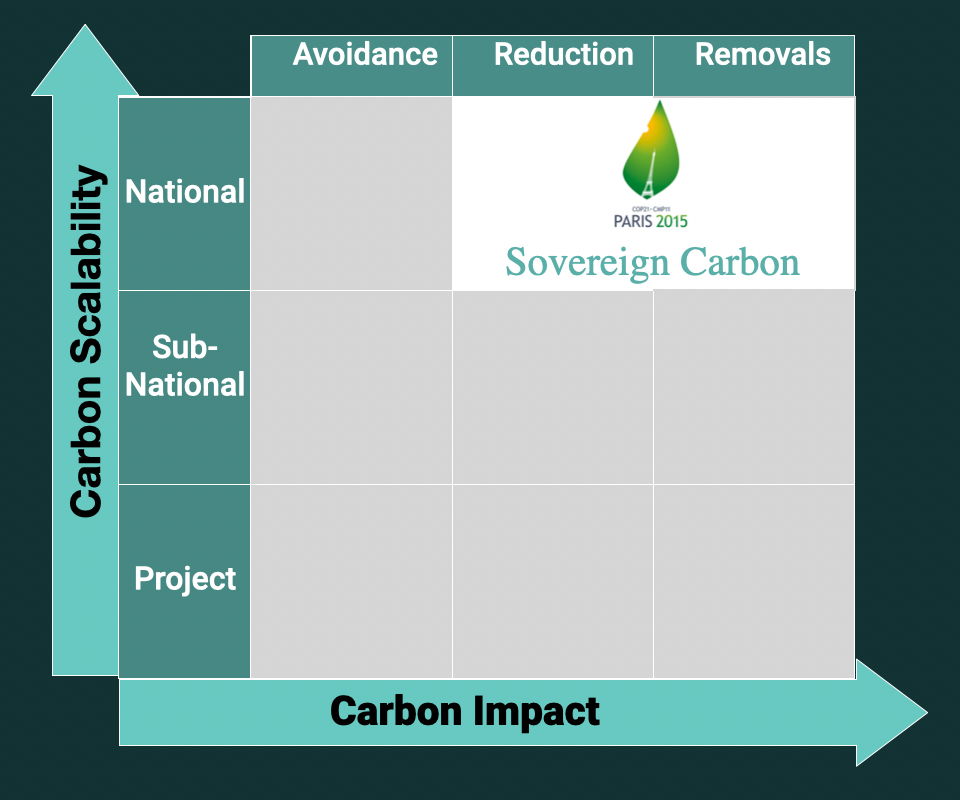
Source & Credits: ITMO Ltd.
Sovereign Carbon Attributes

Sovereign Carbon White Paper
In October 2022, Deutsche Bank, the Coalition for Rainforest Nations, and the ITMO team published the first White Paper on Sovereign Carbon.
Download it here >>
Download press release>>
Source & Credits: Deutsche Bank, Coalition for Rainforest Nations and ITMO Ltd.
